http://blog.csdn.net/droidphone/article/details/7975694
clock source用于为Linux内核提供一个时间基线,如果你用linux的date命令获取当前时间,内核会读取当前的clock source,转换并返回合适的时间单位给用户空间。在硬件层,它通常实现为一个由固定时钟频率驱动的计数器,计数器只能单调地增加,直到溢出为止。时钟源是内核计时的基础,系统启动时,内核通过硬件RTC获得当前时间,在这以后,在大多数情况下,内核通过选定的时钟源更新实时时间信息(墙上时间),而不再读取RTC的时间。本节的内核代码树基于V3.4.10。
1. struct clocksource结构
内核用一个clocksource结构对真实的时钟源进行软件抽象,现在我们从clock source的数据结构开始,它的定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
struct clocksource {
/*
* Hotpath data, fits in a single cache line when the
* clocksource itself is cacheline aligned.
*/
cycle_t (*read)(struct clocksource *cs);
cycle_t cycle_last;
cycle_t mask;
u32 mult;
u32 shift;
u64 max_idle_ns;
u32 maxadj;
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_CLOCKSOURCE_DATA
struct arch_clocksource_data archdata;
#endif
const char *name;
struct list_head list;
int rating;
int (*enable)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*disable)(struct clocksource *cs);
unsigned long flags;
void (*suspend)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*resume)(struct clocksource *cs);
/* private: */
#ifdef CONFIG_CLOCKSOURCE_WATCHDOG
/* Watchdog related data, used by the framework */
struct list_head wd_list;
cycle_t cs_last;
cycle_t wd_last;
#endif
} ____cacheline_aligned;
ocksource中的几个重要的字段。
1.1 rating:时钟源的精度
同一个设备下,可以有多个时钟源,每个时钟源的精度由驱动它的时钟频率决定,比如一个由10MHz时钟驱动的时钟源,他的精度就是100nS。clocksource结构中有一个rating字段,代表着该时钟源的精度范围,它的取值范围如下:
1
2
3
4
5
1--99: 不适合于用作实际的时钟源,只用于启动过程或用于测试;
100--199:基本可用,可用作真实的时钟源,但不推荐;
200--299:精度较好,可用作真实的时钟源;
300--399:很好,精确的时钟源;
400--499:理想的时钟源,如有可能就必须选择它作为时钟源;
1.2 read回调函数
时钟源本身不会产生中断,要获得时钟源的当前计数,只能通过主动调用它的read回调函数来获得当前的计数值,注意这里只能获得计数值,也就是所谓的cycle,要获得相应的时间,必须要借助clocksource的mult和shift字段进行转换计算。
1.3 mult和shift字段
因为从clocksource中读到的值是一个cycle计数值,要转换为时间,我们必须要知道驱动clocksource的时钟频率F,一个简单的计算就可以完成:
可是clocksource并没有保存时钟的频率F,因为使用上面的公式进行计算,需要使用浮点运算,这在内核中是不允许的,因此,内核使用了另外一个变通的办法,根据时钟的频率和期望的精度,事先计算出两个辅助常数mult和shift,然后使用以下公式进行cycle和t的转换:
1
t = (cycle * mult) >> shift;
只要我们保证:
1
F = (1 << shift) / mult;
内核内部使用64位进行该转换计算:
1
2
3
4
static inline s64 clocksource_cyc2ns(cycle_t cycles, u32 mult, u32 shift)
{
return ((u64) cycles * mult) >> shift;
}
从转换精度考虑,mult的值是越大越好,但是为了计算过程不发生溢出,mult的值又不能取得过大。为此内核假设cycle计数值被转换后的最大时间值:10分钟(600秒),主要的考虑是CPU进入IDLE状态后,时间信息不会被更新,只要在10分钟内退出IDLE,clocksource的cycle计数值就可以被正确地转换为相应的时间,然后系统的时间信息可以被正确地更新。当然最后的结果不一定是10分钟,它由clocksource_max_deferment进行计算,并保存max_idle_ns字段中,tickless的代码要考虑这个值,以防止在NO_HZ配置环境下,系统保持IDLE状态的时间过长。在这样,由10分钟这个假设的时间值,我们可以推算出合适的mult和shift值。
2. clocksource的注册和初始化
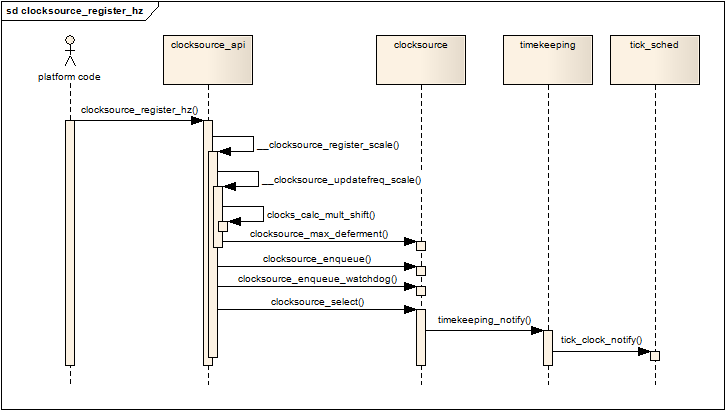
通常,clocksource要在初始化阶段通过clocksource_register_hz函数通知内核它的工作时钟的频率,调用的过程如下:
由上图可见,最终大部分工作会转由__clocksource_register_scale完成,该函数首先完成对mult和shift值的计算,然后根据mult和shift值,最终通过clocksource_max_deferment获得该clocksource可接受的最大IDLE时间,并记录在clocksource的max_idle_ns字段中。clocksource_enqueue函数负责按clocksource的rating的大小,把该clocksource按顺序挂在全局链表clocksource_list上,rating值越大,在链表上的位置越靠前。
每次新的clocksource注册进来,都会触发clocksource_select函数被调用,它按照rating值选择最好的clocksource,并记录在全局变量curr_clocksource中,然后通过timekeeping_notify函数通知timekeeping,当前clocksource已经变更,关于timekeeping,我将会在后续的博文中阐述。
3. clocksource watchdog
系统中可能同时会注册对个clocksource,各个clocksource的精度和稳定性各不相同,为了筛选这些注册的clocksource,内核启用了一个定时器用于监控这些clocksource的性能,定时器的周期设为0.5秒:
1
2
#define WATCHDOG_INTERVAL (HZ >> 1)
#define WATCHDOG_THRESHOLD (NSEC_PER_SEC >> 4)
当有新的clocksource被注册时,除了会挂在全局链表clocksource_list外,还会同时挂在一个watchdog链表上:watchdog_list。定时器周期性地(0.5秒)检查watchdog_list上的clocksource,WATCHDOG_THRESHOLD的值定义为0.0625秒,如果在0.5秒内,clocksource的偏差大于这个值就表示这个clocksource是不稳定的,定时器的回调函数通过clocksource_watchdog_kthread线程标记该clocksource,并把它的rate修改为0,表示精度极差。
4. 建立clocksource的简要过程
在系统的启动阶段,内核注册了一个基于jiffies的clocksource,代码位于kernel/time/jiffies.c:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
struct clocksource clocksource_jiffies = {
.name = "jiffies",
.rating = 1, /* lowest valid rating*/
.read = jiffies_read,
.mask = 0xffffffff, /*32bits*/
.mult = NSEC_PER_JIFFY << JIFFIES_SHIFT, /* details above */
.shift = JIFFIES_SHIFT,
};
......
static int __init init_jiffies_clocksource(void)
{
return clocksource_register(&clocksource_jiffies);
}
core_initcall(init_jiffies_clocksource);
它的精度只有1/HZ秒,rating值为1,如果平台的代码没有提供定制的clocksource_default_clock函数,它将返回该clocksource:
1
2
3
4
struct clocksource * __init __weak clocksource_default_clock(void)
{
return &clocksource_jiffies;
}
然后,在初始化的后段,clocksource的代码会把全局变量curr_clocksource设置为上述的clocksource:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
static int __init clocksource_done_booting(void)
{
......
curr_clocksource = clocksource_default_clock();
......
finished_booting = 1;
......
clocksource_select();
......
return 0;
}
fs_initcall(clocksource_done_booting);
当然,如果平台级的代码在初始化时也会注册真正的硬件clocksource,所以经过clocksource_select()函数后,curr_clocksource将会被设为最合适的clocksource。如果clocksource_select函数认为需要切换更好的时钟源,它会通过timekeeping_notify通知timekeeping系统,使用新的clocksource进行时间计数和更新操作。