/etc/my.cnf
增加:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |


增加:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
1 2 3 4 5 | |
sk 的slab初始化的时候带上 SLAB_DESTROY_BY_RCU ,所以free(sk)只会把sk加入到slab的freelist,并不会释放内存。
这也就是为什么__inet_lookup_established里需要两次INET_MATCH。因为第一次INET_MATCH到atomic_inc_not_zero之间有可能在另一个cpu上将sk放到freelist,然后sk又被其他连接alloc拿去用了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | |
https://blog.csdn.net/dog250/article/details/73013732
我们已经知道,在TCP的接收主函数tcp_v4_rcv中,基于skb的元数据查找socket的过程是无锁的,查找完毕之后,会针对找到的socket结果上锁或者无锁处理,逻辑非常清晰:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
这个逻辑已经臻于完美了,至少在表面上看来确实如此!
当我知道了4.7内核针对syncookie的优化之后,我便内窥了lockless_lookup内部,突破性的改进在于,4.7内核用真正的RCU callback替换了一个仅有的Atomic操作,做到了真正的无锁化查找!
看来我们都被骗了,其实所谓的lockless_lookup并不是真正的lockless,为了应景和应题,本文只讨论Listener socket,我们来看下它的逻辑:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | |
这个逻辑可以分为3个部分,我在注释中已经标明,可以看到,虽然在调用者tcp_v4_rcv看来,查找socket的操作是无锁的,然而内窥其实现逻辑之后便会发现,它其实还是在内部进行了两个轻量级的互斥操作。下面我来一个一个说。
由于在lockless_lookup被调用时是无锁的,所以在sk_nulls_for_each_rcu遍历过程中会出现以下情况造成遍历混乱:
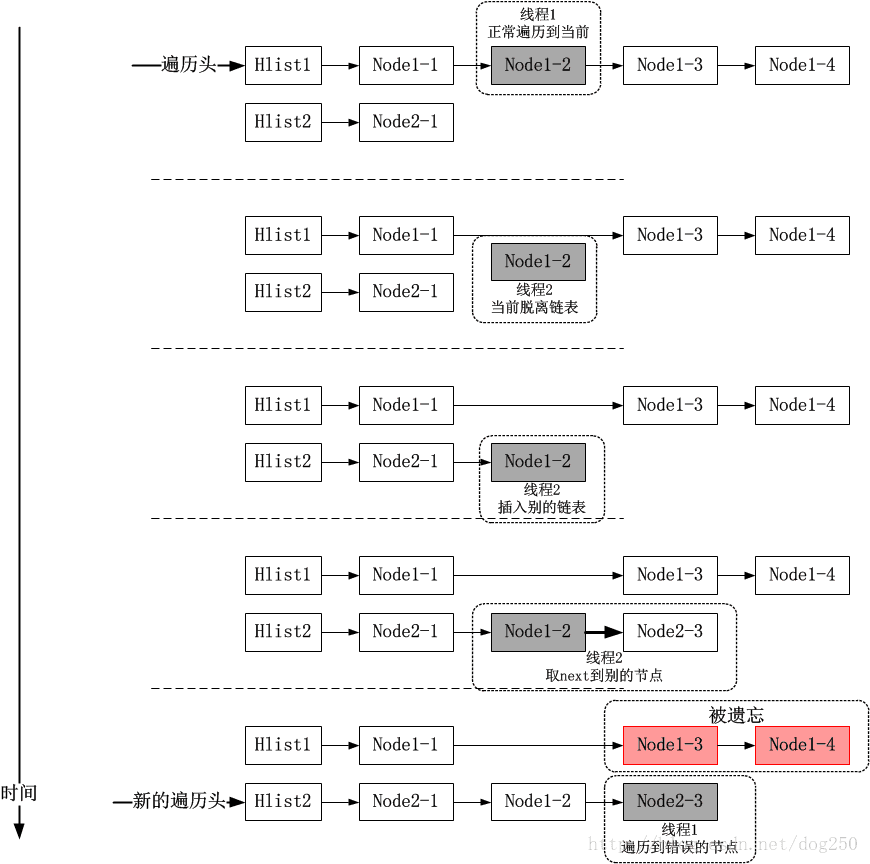
这种情况下,常规的hlist是无法发现的,因为这种hlist以next为NULL视为链表的结束。不管一个node被重新hash到哪个链表,在结束的时候都会碰到NULL,此时你根本区别不出来这个NULL是不是一开始遍历开始时那个hlist冲突链表的NULL。怎么解决这个问题呢?上锁肯定是不妥的,幸亏Linux内核有一个精妙的数据结构,即nulls hlist!下面我先来简单地介绍一下这个精妙的hlist数据结构和标准的hlist有何不同。
1.nulls hlist不再以NULL结尾,而以一个大到231空间的任意值结尾
2.nulls hlist以node最低位是不是1标识是不是链表的结束
于是nulls hlist的结尾节点的next字段可以编码为高31位和低1位,如果低1位为1,那么高31位便可以取出当初存进去的任意值,是不是很精妙呢?!之所以可以这么做,原因很简单,在计算机中,Linux内核数据结构的所有的地址都是对齐存放的,因此最低1位的数据位是空闲的,当然可以借为它用了。
现在我们考虑这个nulls node的高31位存什么数据好呢?答案很明确,当然是存该hlist的hash值了,这样以下的操作一目了然:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | |
是不是很精妙呢?其实在Linux中,很多地方都用到了这个nulls hlist数据结构,我第一次看到它是在当年搞nf conntrack的时候。 以上的叙述大致解释了这个nulls hlist的精妙之处,说完了优点再看看它的问题,这个nulls hlist带啦的不断retry是一种消极尝试,非常类似顺序锁读操作,只要读冲突便一直重复,直到某次没有冲突,关于顺序锁,可以看一下read_seqbegin/read_seqretry以及write_seqlock这对夫妻和小三。 为什么需要这样?答案是,在无锁化的lookup中,必须这样!因为你取出一个node和从该node取出下一个node之间是有时间差的,你没有对这个时间差强制没有任何保护措施,这就是根本原因,所以,消极的尝试也未尝不是一个好办法。 总结下根本原因,取出node和取出下一个node之间存在race!
刚刚说完了lockless_lookup的第二部分,下面看看第三部分,atomic_inc_not_zero带来的互斥。
我们知道,在sk_nulls_for_each_rcu找到一个匹配的socket并且nulls node检查通过之后,在实际使用它之前,由于无锁化调用,会存在race,此期间可能会有别的线程将该socket释放到虚空,如何避免使用一个已经被释放的socket呢?这个很简单,操作原子计数器即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | |
虽然这个Atomic变量不是什么锁,但是在微观上,操作它是要锁总线的,即便在代码层面没有看到任何lock字眼,但这是指令集的逻辑。当面对ddos攻击的时候,试想同时会有多少的线程争抢这个Atomic底下的总线资源!!这是一笔昂贵的开销!
为什么非要有这么一个操作呢?答案很明确,怕取到一个被释放的socket从而导致内核数据混乱,简单点说就是怕panic。所以必然要有个原子变量来保护一下,事实证明,这么做还真不错呢。然而把问题更上一层来谈,为什么内核数据会混乱导致panic?因为取出node和使用node之间存在race,在这两个操作之间,node可能会被释放掉。这一点和上面的“取出node和取出下一个node之间存在race”是不同的。
1.取出node和取出下一个node之间;
2.取出node和使用node之间。
但归根结底,这两个race是同一个问题导致,那就是socket被释放(重新hash也有个先被释放的过程)!如果一个socket在被lookup期间,不允许被释放是否可以呢(你可以调用释放操作,但在此期间,你要保证数据有效)?当然可以,如何做到就是一个简单的事情了。如果能做到这一点并且真的做了,上述针对两个race的两个互斥就可以去掉了,TCP的新建连接数性能指标必然会有大幅度提升。
Linux 4.7内核通过SOCK_RCU_FREE标识重构了sk_destruct的实现:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
如果携带有SOCK_RCU_FREE标识,便通过RCU callback进行释放,我们知道,RCU callback的调用时机是必须经过一个grace period,而这个period通过rcu lock/unlock可以严格控制。
一切显得简单明了。Linux 4.7内核仅为Listener socket设置了SOCK_RCU_FREE标识:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | |
这保证了在lockless_lookup调用中不必再担心取到错误的数据和无效的数据,前提是lockless_lookup的调用必须有rcu锁的保护。这很容易:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
当然,这个lock/unlock没有体现在tcp_v4_rcv函数里,而是体现在了ip_local_deliver_finish里。
以下是一个社区的patch:
[PATCH v2 net-next 06/11] tcp/dccp: do not touch listener sk_refcnt under synflood
http://www.spinics.net/lists/netdev/msg371229.html
本地下载 do-not-touch-listener-sk_refcnt-under-synflood.patch
作者详细说明了取消原子变量操作后带来的收益并且携带测试结果,我想这算是令人信服的,最重要的是,它已经被合入内核了。
crash执行shell脚本
1 2 3 4 5 | |