http://my.oschina.net/kisops/blog/150995
解决:nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
“连接跟踪表已满,开始丢包”!相信不少用iptables的同学都会见过这个错误信息吧,这个问题曾经也困扰过我好长一段时间。此问题的解决办法有四种(nf_conntrack 在CentOS 5 / kernel <= 2.6.19中名为 ip_conntrack ):
一、关闭防火墙。 简单粗暴,直接有效
1
2
3
4
chkconfig iptables off
chkconfig ip6tables off
service iptables stop
service ip6tables stop
切记:在防火墙关闭状态下,不要通过iptables指令(比如 iptables -nL)来查看当前状态!因为这样会导致防火墙被启动,而且规则为空。虽然不会有任何拦截效果,但所有连接状态都会被记录,浪费资源且影响性能并可能导致防火墙主动丢包!
二、加大防火墙跟踪表的大小,优化对应的系统参数
1、状态跟踪表的最大行数的设定,理论最大值 CONNTRACK_MAX = RAMSIZE (in bytes) / 16384 / (ARCH / 32)
以64G的64位操作系统为例,CONNTRACK_MAX = 641024 1024*1024/16384/2 = 2097152
即时生效请执行:
1
sysctl -w net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 2097152
2、其哈希表大小通常为总表的1/8,最大为1/2。
CONNTRACK_BUCKETS = CONNTRACK_MAX / 8
同样64G的64位操作系统,哈希最佳范围是 262144 ~ 1048576 。
运行状态中通过 sysctl net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_buckets 进行查看,通过文件 /sys/module/nf_conntrack/parameters/hashsize 进行设置
或者新建 /etc/modprobe.d/iptables.conf ,重新加载模块才生效:
1
options nf_conntrack hashsize = 262144
3、还有些相关的系统参数sysctl -a | grep nf_conntrack可以调优(/etc/sysctl.conf ):
1
2
3
4
5
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 1048576
net.netfilter.ip_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 3600
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120
三、使用祼表,添加“不跟踪”标识。如下示例更适合桌面系统或随意性强的服务器。因为它开启了连接的状态机制,方便和外部通信。修改 /etc/sysconfig/iptables 文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
*raw
# 对TCP连接不启用追踪,解决ip_contrack满导致无法连接的问题
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j NOTRACK
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j NOTRACK
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 21 -j NOTRACK
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 11211 -j NOTRACK
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --dport 60000:60100 -j NOTRACK
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -s 192.168.10.1 -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp --sport 80 -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp --sport 21 -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp --sport 11211 -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -m tcp --sport 60000:60100 -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -s 192.168.10.1 -j NOTRACK
COMMIT
*filter
# 允许ping
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
# 对本地回路、第5张网卡放行
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth4 -j ACCEPT
# 连接状态跟踪,已建立的连接允许传输数据
-A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED,INVALID,UNTRACKED -j ACCEPT
# filter表里存在但在raw里不存在的,默认会进行连接状态跟踪
-A INPUT -s 192.168.10.31 -p tcp --dport 2669 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
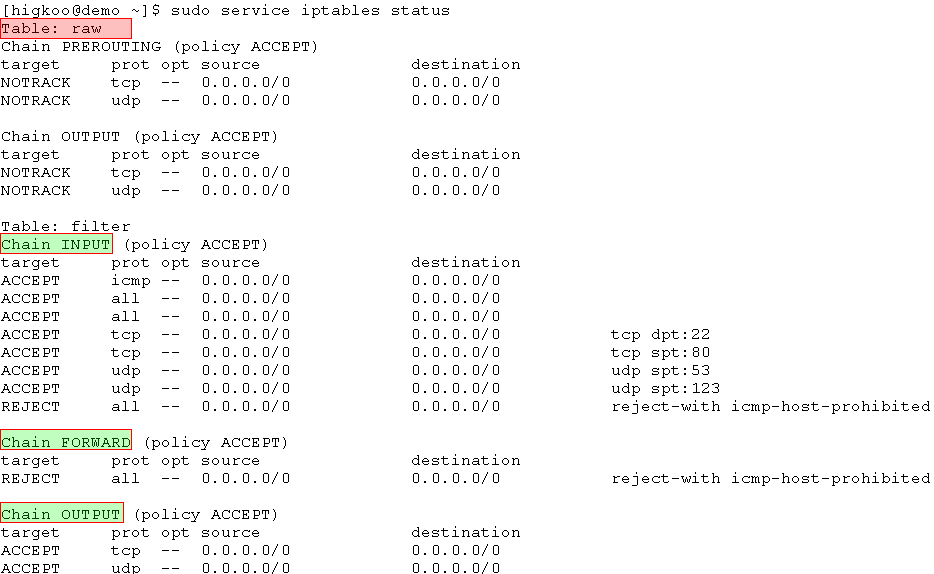
或者干脆对所有连接都关闭跟踪,不跟踪任何连接状态。不过规则就限制比较严谨,进出都需要显式申明。示例 /etc/sysconfig/iptables :
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
*raw
# 对TCP/UDP连接不启用追踪,解决nf_contrack满导致无法连接的问题
-A PREROUTING -p tcp -j NOTRACK
-A PREROUTING -p udp -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -j NOTRACK
-A OUTPUT -p udp -j NOTRACK
COMMIT
*filter
# 允许ping
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
# 对本地回路和eth1放行
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth1 -j ACCEPT
# 只允许符合条件的连接进行传输数据
-A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p tcp --sport 80 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p udp --sport 53 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p udp --sport 123 -j ACCEPT
# 出去的包都不限制
-A OUTPUT -p tcp -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -p udp -j ACCEPT
# 输入和转发的包不符合规则的全拦截
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
效果如下图:
四、删除连接跟踪模块lsmod | grep nf_conntrack,不使用连接状态的跟踪功能。
1、删除nf_conntrack和相关的依赖模块,示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
rmmod nf_conntrack_ipv4
rmmod nf_conntrack_ipv6
rmmod xt_state
rmmod xt_CT
rmmod xt_conntrack
rmmod iptable_nat
rmmod ipt_REDIRECT
rmmod nf_nat
rmmod nf_conntrack
2、禁用跟踪模块,把它加到黑名单(/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf ):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 禁用 nf_conntrack 模块
blacklist nf_conntrack
blacklist nf_conntrack_ipv6
blacklist xt_conntrack
blacklist nf_conntrack_ftp
blacklist xt_state
blacklist iptable_nat
blacklist ipt_REDIRECT
blacklist nf_nat
blacklist nf_conntrack_ipv4
3、去掉防火墙里所有和状态相关的配置(比如state状态,NAT功能),示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
*filter
# 允许ping
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
# 对本地回路和第2张网卡放行
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i eth1 -j ACCEPT
# 对端口放行
-A INPUT -p tcp --dport 1331 -j ACCEPT
# 对IP放行
-A INPUT -s 192.168.10.31 -j ACCEPT
#允许本机进行DNS查询
-A INPUT -p udp --sport 53 -j ACCEPT
-A OUTPUT -p udp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
另外,防火墙的配置文件最好也改下,不要加载任何额外模块(/etc/sysconfig/iptables-config):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
IPTABLES_MODULES="" # 不需要任何附加模块
IPTABLES_MODULES_UNLOAD="no" # 避免iptables重启后sysctl中对应的参数被重置为系统默认值
IPTABLES_SAVE_ON_STOP="no"
IPTABLES_SAVE_ON_RESTART="no"
IPTABLES_SAVE_COUNTER="no"
IPTABLES_STATUS_NUMERIC="yes"
IPTABLES_STATUS_VERBOSE="no"
IPTABLES_STATUS_LINENUMBERS="no"
往往我们对连接的跟踪都是基于操作系统的(netstat / ss ),防火墙的连接状态完全是它自身实现产生的。
总结:防火墙有条件还是交给上层设备完成会更好,使用防火墙一定要做调优;如果不需要防火墙的跟踪功能,规则简单的可以开启NOTRACK选项,条件允许的情况下就删除它吧!