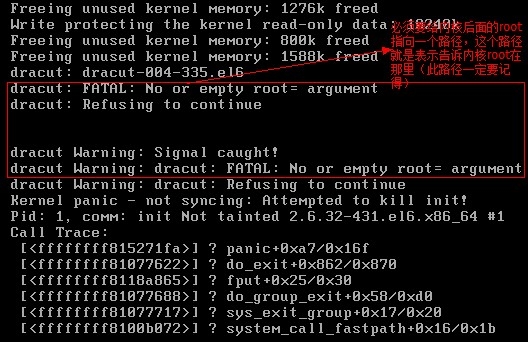
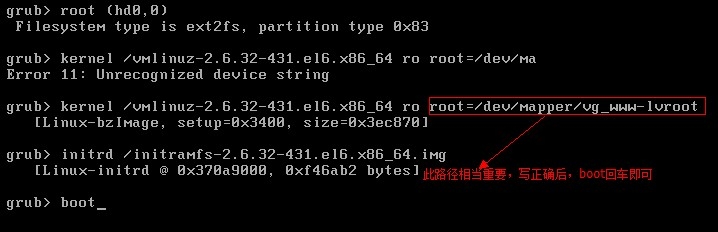
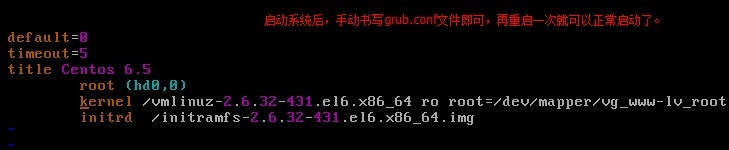
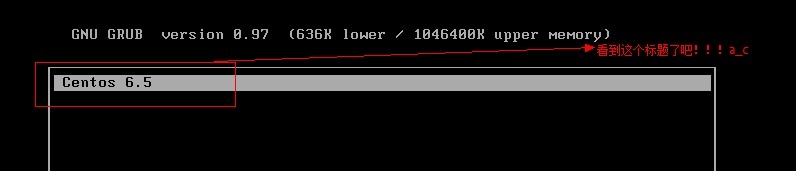
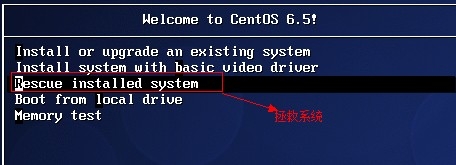
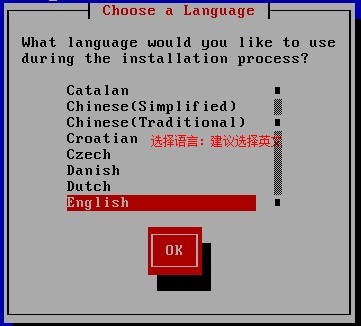
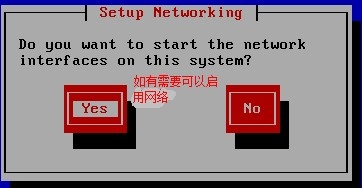
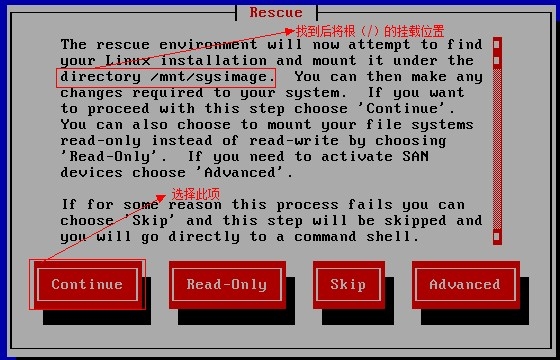
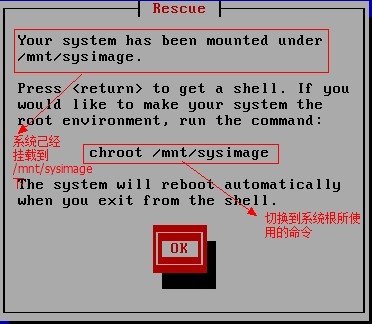
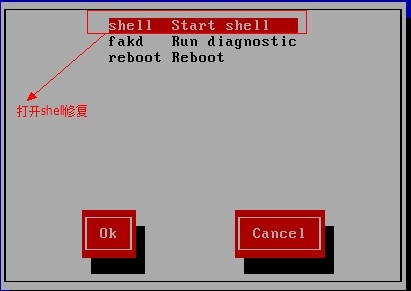
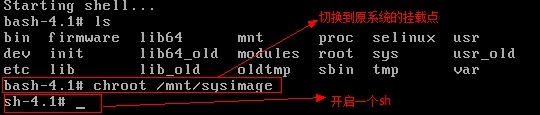
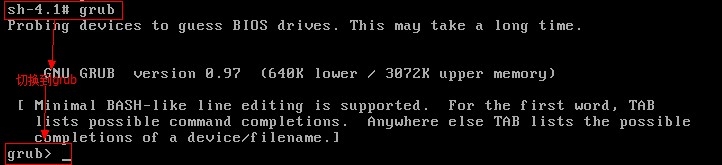
http://www.cnblogs.com/Neddy/archive/2012/02/03/2336698.html
ARM汇编指令集
一、 跳转指令
跳转指令用于实现程序流程的跳转,在ARM程序中有两种方法可以实现程序流程的跳转:
Ⅰ.使用专门的跳转指令。
Ⅱ.直接向程序计数器PC写入跳转地址值。
通过向程序计数器PC写入跳转地址值,可以实现在4GB的地址空间中的任意跳转,在跳转之前结合使用
MOV LR,PC
等类似指令,可以保存将来的返回地址值,从而实现在4GB连续的线性地址空间的子程序调用。
ARM指令集中的跳转指令可以完成从当前指令向前或向后的32MB的地址空间的跳转,包括以下4条指令:
1、 B指令
B指令的格式为:
B{条件} 目标地址
B指令是最简单的跳转指令。一旦遇到一个 B 指令,ARM 处理器将立即跳转到给定的目标地址,从那里继续执行。注意存储在跳转指令中的实际值是相对当前PC值的一个偏移量,而不是一个绝对地址,它的值由汇编器来计算(参考寻址方式中的相对寻址)。它是 24 位有符号数,左移两位后有符号扩展为 32 位,表示的有效偏移为 26 位(前后32MB的地址空间)。以下指令:
1 2 3 | |
2、 BL指令
BL指令的格式为:
BL{条件} 目标地址
BL 是另一个跳转指令,但跳转之前,会在寄存器R14中保存PC的当前内容,因此,可以通过将R14 的内容重新加载到PC中,来返回到跳转指令之后的那个指令处执行。该指令是实现子程序调用的一个基本但常用的手段。以下指令:
1
| |
3、 BLX指令
BLX指令的格式为:
BLX 目标地址
BLX指令从ARM指令集跳转到指令中所指定的目标地址,并将处理器的工作状态有ARM状态切换到Thumb状态,该指令同时将PC的当前内容保存到寄存器R14中。因此,当子程序使用Thumb指令集,而调用者使用ARM指令集时,可以通过BLX指令实现子程序的调用和处理器工作状态的切换。同时,子程序的返回可以通过将寄存器R14值复制到PC中来完成。
4、 BX指令
BX指令的格式为:
BX{条件} 目标地址
BX指令跳转到指令中所指定的目标地址,目标地址处的指令既可以是ARM指令,也可以是Thumb指令。
二、数据处理指令数据处理指令可分为数据传送指令、算术逻辑运算指令和比较指令等。
数据传送指令用于在寄存器和存储器之间进行数据的双向传输。
算术逻辑运算指令完成常用的算术与逻辑的运算,该类指令不但将运算结果保存在目的寄存器中,同时更新CPSR中的相应条件标志位。
比较指令不保存运算结果,只更新CPSR中相应的条件标志位。
数据处理指令共以下16条。
1、 MOV指令
MOV指令的格式为:
MOV{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,源操作数
MOV指令可完成从另一个寄存器、被移位的寄存器或将一个立即数加载到目的寄存器。其中S选项决定指令的操作是否影响CPSR中条件标志位的值,当没有S时指令不更新CPSR中条件标志位的值。
指令示例:
1 2 3 | |
2、 MVN指令
MVN指令的格式为:
MVN{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,源操作数
MVN指令可完成从另一个寄存器、被移位的寄存器、或将一个立即数加载到目的寄存器。与MOV指令不同之处是在传送之前按位被取反了,即把一个被取反的值传送到目的寄存器中。其中S决定指令的操作是否影响CPSR中条件标志位的值,当没有S时指令不更新CPSR中条件标志位的值。
指令示例:
1
| |
3、 CMP指令
CMP指令的格式为:
CMP{条件} 操作数1,操作数2
CMP指令用于把一个寄存器的内容和另一个寄存器的内容或立即数进行比较,同时更新CPSR中条件标志位的值。该指令进行一次减法运算,但不存储结果,只更改条件标志位。标志位表示的是操作数1与操作数2的关系(大、小、相等),例如,当操作数1大于操作操作数2,则此后的有GT 后缀的指令将可以执行。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
4、 CMN指令
CMN指令的格式为:
CMN{条件} 操作数1,操作数2
CMN指令用于把一个寄存器的内容和另一个寄存器的内容或立即数取反后进行比较,同时更新CPSR中条件标志位的值。该指令实际完成操作数1和操作数2相加,并根据结果更改条件标志位。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
5、 TST指令
TST指令的格式为:
TST{条件} 操作数1,操作数2
TST指令用于把一个寄存器的内容和另一个寄存器的内容或立即数进行按位的与运算,并根据运算结果更新CPSR中条件标志位的值。操作数1是要测试的数据,而操作数2是一个位掩码,该指令一般用来检测是否设置了特定的位。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
6、 TEQ指令
TEQ指令的格式为:
TEQ{条件} 操作数1,操作数2
TEQ指令用于把一个寄存器的内容和另一个寄存器的内容或立即数进行按位的异或运算,并根据运算结果更新CPSR中条件标志位的值。该指令通常用于比较操作数1和操作数2是否相等。
指令示例:
1
| |
7、 ADD指令
ADD指令的格式为:
ADD{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
ADD指令用于把两个操作数相加,并将结果存放到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。
指令示例:
1 2 3 | |
8、 ADC指令
ADC指令的格式为:
ADC{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
ADC指令用于把两个操作数相加,再加上CPSR中的C条件标志位的值,并将结果存放到目的寄存器中。它使用一个进位标志位,这样就可以做比32位大的数的加法,注意不要忘记设置S后缀来更改进位标志。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。
以下指令序列完成两个128位数的加法,第一个数由高到低存放在寄存器R7~R4,第二个数由高到低存放在寄存器R11~R8,运算结果由高到低存放在寄存器R3~R0:
1 2 3 4 | |
9、 SUB指令
SUB指令的格式为:
SUB{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
SUB指令用于把操作数1减去操作数2,并将结果存放到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。该指令可用于有符号数或无符号数的减法运算。
指令示例:
1 2 3 | |
10、C指令
C指令的格式为:
C{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
C指令用于把操作数1减去操作数2,再减去CPSR中的C条件标志位的反码,并将结果存放到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。该指令使用进位标志来表示借位,这样就可以做大于32位的减法,注意不要忘记设置S后缀来更改进位标志。该指令可用于有符号数或无符号数的减法运算。
指令示例:
1
| |
11、R指令
R指令的格式为:
R{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
R指令称为逆向减法指令,用于把操作数2减去操作数1,并将结果存放到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。该指令可用于有符号数或无符号数的减法运算。
指令示例:
1 2 3 | |
12、RSC指令
RSC指令的格式为:
RSC{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
RSC指令用于把操作数2减去操作数1,再减去CPSR中的C条件标志位的反码,并将结果存放到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。该指令使用进位标志来表示借位,这样就可以做大于32位的减法,注意不要忘记设置S后缀来更改进位标志。该指令可用于有符号数或无符号数的减法运算。
指令示例:
1
| |
13、AND指令
AND指令的格式为:
AND{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
AND指令用于在两个操作数上进行逻辑与运算,并把结果放置到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。该指令常用于屏蔽操作数1的某些位。
指令示例:
1
| |
14、ORR指令
ORR指令的格式为:
ORR{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
ORR指令用于在两个操作数上进行逻辑或运算,并把结果放置到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。该指令常用于设置操作数1的某些位。
指令示例:
1
| |
15、EOR指令
EOR指令的格式为:
EOR{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
EOR指令用于在两个操作数上进行逻辑异或运算,并把结果放置到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。该指令常用于反转操作数1的某些位。
指令示例:
1
| |
16、BIC指令
BIC指令的格式为:
BIC{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
BIC指令用于清除操作数1的某些位,并把结果放置到目的寄存器中。操作数1应是一个寄存器,操作数2可以是一个寄存器,被移位的寄存器,或一个立即数。操作数2为32位的掩码,如果在掩码中设置了某一位,则清除这一位。未设置的掩码位保持不变。
指令示例:
1
| |
三、乘法指令与乘加指令
ARM微处理器支持的乘法指令与乘加指令共有6条,可分为运算结果为32位和运算结果为64位两类,与前面的数据处理指令不同,指令中的所有操作数、目的寄存器必须为通用寄存器,不能对操作数使用立即数或被移位的寄存器,同时,目的寄存器和操作数1必须是不同的寄存器。
乘法指令与乘加指令共有以下6条:
1、 MUL指令
MUL指令的格式为:
MUL{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2
MUL指令完成将操作数1与操作数2的乘法运算,并把结果放置到目的寄存器中,同时可以根据运算结果设置CPSR中相应的条件标志位。其中,操作数1和操作数2均为32位的有符号数或无符号数。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
2、 MLA指令
MLA指令的格式为:
MLA{条件}{S} 目的寄存器,操作数1,操作数2,操作数3
MLA指令完成将操作数1与操作数2的乘法运算,再将乘积加上操作数3,并把结果放置到目的寄存器中,同时可以根据运算结果设置CPSR中相应的条件标志位。其中,操作数1和操作数2均为32位的有符号数或无符号数。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
3、 SMULL指令
SMULL指令的格式为:
SMULL{条件}{S} 目的寄存器Low,目的寄存器低High,操作数1,操作数2
SMULL指令完成将操作数1与操作数2的乘法运算,并把结果的低32位放置到目的寄存器Low中,结果的高32位放置到目的寄存器High中,同时可以根据运算结果设置CPSR中相应的条件标志位。其中,操作数1和操作数2均为32位的有符号数。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
4、 SMLAL指令
SMLAL指令的格式为:
SMLAL{条件}{S} 目的寄存器Low,目的寄存器低High,操作数1,操作数2
SMLAL指令完成将操作数1与操作数2的乘法运算,并把结果的低32位同目的寄存器Low中的值相加后又放置到目的寄存器Low中,结果的高32位同目的寄存器High中的值相加后又放置到目的寄存器High中,同时可以根据运算结果设置CPSR中相应的条件标志位。其中,操作数1和操作数2均为32位的有符号数。
对于目的寄存器Low,在指令执行前存放64位加数的低32位,指令执行后存放结果的低32位。
对于目的寄存器High,在指令执行前存放64位加数的高32位,指令执行后存放结果的高32位。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
5、 UMULL指令
UMULL指令的格式为:
UMULL{条件}{S} 目的寄存器Low,目的寄存器低High,操作数1,操作数2
UMULL指令完成将操作数1与操作数2的乘法运算,并把结果的低32位放置到目的寄存器Low中,结果的高32位放置到目的寄存器High中,同时可以根据运算结果设置CPSR中相应的条件标志位。其中,操作数1和操作数2均为32位的无符号数。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
6、 UMLAL指令
UMLAL指令的格式为:
UMLAL{条件}{S} 目的寄存器Low,目的寄存器低High,操作数1,操作数2
UMLAL指令完成将操作数1与操作数2的乘法运算,并把结果的低32位同目的寄存器Low中的值相加后又放置到目的寄存器Low中,结果的高32位同目的寄存器High中的值相加后又放置到目的寄存器High中,同时可以根据运算结果设置CPSR中相应的条件标志位。其中,操作数1和操作数2均为32位的无符号数。
对于目的寄存器Low,在指令执行前存放64位加数的低32位,指令执行后存放结果的低32位。
对于目的寄存器High,在指令执行前存放64位加数的高32位,指令执行后存放结果的高32位。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
四、程序状态寄存器访问指令
1、 MRS指令
MRS指令的格式为:
MRS{条件} 通用寄存器,程序状态寄存器(CPSR或SPSR)
MRS指令用于将程序状态寄存器的内容传送到通用寄存器中。该指令一般用在以下两种情况:
Ⅰ.当需要改变程序状态寄存器的内容时,可用MRS将程序状态寄存器的内容读入通用寄存器,修改后再写回程序状态寄存器。
Ⅱ.当在异常处理或进程切换时,需要保存程序状态寄存器的值,可先用该指令读出程序状态寄存器的值,然后保存。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
2、 MSR指令
MSR指令的格式为:
MSR{条件} 程序状态寄存器(CPSR或SPSR)_<域>,操作数
MSR指令用于将操作数的内容传送到程序状态寄存器的特定域中。其中,操作数可以为通用寄存器或立即数。<域>用于设置程序状态寄存器中需要操作的位,32位的程序状态寄存器可分为4个域:
位[31:24]为条件标志位域,用f表示;
位[23:16]为状态位域,用s表示;
位[15:8]为扩展位域,用x表示;
位[7:0]为控制位域,用c表示;
该指令通常用于恢复或改变程序状态寄存器的内容,在使用时,一般要在MSR指令中指明将要操作的域。
指令示例:
1 2 3 | |
五、加载/存储指令
ARM微处理器支持加载/存储指令用于在寄存器和存储器之间传送数据,加载指令用于将存储器中的数据传送到寄存器,存储指令则完成相反的操作。常用的加载存储指令如下:
1、LDR指令
LDR指令的格式为:
LDR{条件} 目的寄存器,<存储器地址>
LDR指令用于从存储器中将一个32位的字数据传送到目的寄存器中。该指令通常用于从存储器中读取32位的字数据到通用寄存器,然后对数据进行处理。当程序计数器PC作为目的寄存器时,指令从存储器中读取的字数据被当作目的地址,从而可以实现程序流程的跳转。该指令在程序设计中比较常用,且寻址方式灵活多样,请读者认真掌握。
指令示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |
2、LDRB指令
LDRB指令的格式为:
LDR{条件}B 目的寄存器,<存储器地址>
LDRB指令用于从存储器中将一个8位的字节数据传送到目的寄存器中,同时将寄存器的高24位清零。该指令通常用于从存储器中读取8位的字节数据到通用寄存器,然后对数据进行处理。当程序计数器PC作为目的寄存器时,指令从存储器中读取的字数据被当作目的地址,从而可以实现程序流程的跳转。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
3、LDRH指令
LDRH指令的格式为:
LDR{条件}H 目的寄存器,<存储器地址>
LDRH指令用于从存储器中将一个16位的半字数据传送到目的寄存器中,同时将寄存器的高16位清零。该指令通常用于从存储器中读取16位的半字数据到通用寄存器,然后对数据进行处理。当程序计数器PC作为目的寄存器时,指令从存储器中读取的字数据被当作目的地址,从而可以实现程序流程的跳转。
指令示例:
1 2 3 | |
4、STR指令
STR指令的格式为:
STR{条件} 源寄存器,<存储器地址>
STR指令用于从源寄存器中将一个32位的字数据传送到存储器中。该指令在程序设计中比较常用,且寻址方式灵活多样,使用方式可参考指令LDR。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
5、STRB指令
STRB指令的格式为:
STR{条件}B 源寄存器,<存储器地址>
STRB指令用于从源寄存器中将一个8位的字节数据传送到存储器中。该字节数据为源寄存器中的低8位。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
6、STRH指令
STRH指令的格式为:
STR{条件}H 源寄存器,<存储器地址>
STRH指令用于从源寄存器中将一个16位的半字数据传送到存储器中。该半字数据为源寄存器中的低16位。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
六、批量数据加载/存储指令
ARM微处理器所支持批量数据加载/存储指令可以一次在一片连续的存储器单元和多个寄存器之间传送数据,批量加载指令用于将一片连续的存储器中的数据传送到多个寄存器,批量数据存储指令则完成相反的操作。
常用的加载存储指令如下:
LDM(或STM)指令
LDM(或STM)指令的格式为:
LDM(或STM){条件}{类型} 基址寄存器{!},寄存器列表{∧}
LDM(或STM)指令用于从由基址寄存器所指示的一片连续存储器到寄存器列表所指示的多个寄存器之间传送数据,该指令的常见用途是将多个寄存器的内容入栈或出栈。其中,{类型}为以下几种情况:
IA 每次传送后地址加1;
IB 每次传送前地址加1;
DA 每次传送后地址减1;
DB 每次传送前地址减1;
FD 满递减堆栈;
ED 空递减堆栈;
FA 满递增堆栈;
EA 空递增堆栈;
{!}为可选后缀,若选用该后缀,则当数据传送完毕之后,将最后的地址写入基址寄存器,否则基址寄存器的内容不改变。
基址寄存器不允许为R15,寄存器列表可以为R0~R15的任意组合。
{∧}为可选后缀,当指令为LDM且寄存器列表中包含R15,选用该后缀时表示:除了正常的数据传送之外,还将SPSR复制到CPSR。同时,该后缀还表示传入或传出的是用户模式下的寄存器,而不是当前模式下的寄存器。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
七、数据交换指令
1、SWP指令
SWP指令的格式为:
SWP{条件} 目的寄存器,源寄存器1,[源寄存器2]
SWP指令用于将源寄存器2所指向的存储器中的字数据传送到目的寄存器中,同时将源寄存器1中的字数据传送到源寄存器2所指向的存储器中。显然,当源寄存器1和目的寄存器为同一个寄存器时,指令交换该寄存器和存储器的内容。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
2、SWPB指令
SWPB指令的格式为:
SWP{条件}B 目的寄存器,源寄存器1,[源寄存器2]
SWPB指令用于将源寄存器2所指向的存储器中的字节数据传送到目的寄存器中,目的寄存器的高24清零,同时将源寄存器1中的字节数据传送到源寄存器2所指向的存储器中。显然,当源寄存器1和目的寄存器为同一个寄存器时,指令交换该寄存器和存储器的内容。
指令示例:
1 2 | |
八、移位指令(操作)
1、LSL(或ASL)操作
LSL(或ASL)操作的格式为:
通用寄存器,LSL(或ASL) 操作数
LSL(或ASL)可完成对通用寄存器中的内容进行逻辑(或算术)的左移操作,按操作数所指定的数量向左移位,低位用零来填充。其中,操作数可以是通用寄存器,也可以是立即数(0~31)。
操作示例
1
| |
2、LSR操作
LSR操作的格式为:
通用寄存器,LSR 操作数
LSR可完成对通用寄存器中的内容进行右移的操作,按操作数所指定的数量向右移位,左端用零来填充。其中,操作数可以是通用寄存器,也可以是立即数(0~31)。
操作示例:
1
| |
3、ASR操作
ASR操作的格式为:
通用寄存器,ASR 操作数
ASR可完成对通用寄存器中的内容进行右移的操作,按操作数所指定的数量向右移位,左端用第31位的值来填充。其中,操作数可以是通用寄存器,也可以是立即数(0~31)。
操作示例:
1
| |
4、ROR操作
ROR操作的格式为:
通用寄存器,ROR 操作数
ROR可完成对通用寄存器中的内容进行循环右移的操作,按操作数所指定的数量向右循环移位,左端用右端移出的位来填充。其中,操作数可以是通用寄存器,也可以是立即数(0~31)。显然,当进行32位的循环右移操作时,通用寄存器中的值不改变。
操作示例:
1
| |
5、RRX操作
RRX操作的格式为:
通用寄存器,RRX 操作数
RRX可完成对通用寄存器中的内容进行带扩展的循环右移的操作,按操作数所指定的数量向右循环移位,左端用进位标志位C来填充。其中,操作数可以是通用寄存器,也可以是立即数(0~31)。
操作示例:
1
| |
九、协处理器指令
1、CDP指令
CDP指令的格式为:
CDP{条件} 协处理器编码,协处理器操作码1,目的寄存器,源寄存器1,源寄存器2,协处理器操作码2。
CDP指令用于ARM处理器通知ARM协处理器执行特定的操作,若协处理器不能成功完成特定的操作,则产生未定义指令异常。其中协处理器操作码1和协处理器操作码2为协处理器将要执行的操作,目的寄存器和源寄存器均为协处理器的寄存器,指令不涉及ARM处理器的寄存器和存储器。
指令示例:
1
| |
2、LDC指令
LDC指令的格式为:
LDC{条件}{L} 协处理器编码,目的寄存器,[源寄存器]
LDC指令用于将源寄存器所指向的存储器中的字数据传送到目的寄存器中,若协处理器不能成功完成传送操作,则产生未定义指令异常。其中,{L}选项表示指令为长读取操作,如用于双精度数据的传输。
指令示例:
1
| |
3、STC指令
STC指令的格式为:
STC{条件}{L} 协处理器编码,源寄存器,[目的寄存器]
STC指令用于将源寄存器中的字数据传送到目的寄存器所指向的存储器中,若协处理器不能成功完成传送操作,则产生未定义指令异常。其中,{L}选项表示指令为长读取操作,如用于双精度数据的传输。
指令示例:
1
| |
4、MCR指令
MCR指令的格式为:
MCR{条件} 协处理器编码,协处理器操作码1,源寄存器,目的寄存器1,目的寄存器2,协处理器操作码2。
MCR指令用于将ARM处理器寄存器中的数据传送到协处理器寄存器中,若协处理器不能成功完成操作,则产生未定义指令异常。其中协处理器操作码1和协处理器操作码2为协处理器将要执行的操作,源寄存器为ARM处理器的寄存器,目的寄存器1和目的寄存器2均为协处理器的寄存器。
指令示例:
1
| |
5、MRC指令
MRC指令的格式为:
MRC{条件} 协处理器编码,协处理器操作码1,目的寄存器,源寄存器1,源寄存器2,协处理器操作码2。
MRC指令用于将协处理器寄存器中的数据传送到ARM处理器寄存器中,若协处理器不能成功完成操作,则产生未定义指令异常。其中协处理器操作码1和协处理器操作码2为协处理器将要执行的操作,目的寄存器为ARM处理器的寄存器,源寄存器1和源寄存器2均为协处理器的寄存器。
指令示例:
1
| |
十、异常产生指令
1、SWI指令
SWI指令的格式为:
SWI{条件} 24位的立即数
SWI指令用于产生软件中断,以便用户程序能调用操作系统的系统例程。操作系统在SWI的异常处理程序中提供相应的系统服务,指令中24位的立即数指定用户程序调用系统例程的类型,相关参数通过通用寄存器传递,当指令中24位的立即数被忽略时,用户程序调用系统例程的类型由通用寄存器R0的内容决定,同时,参数通过其他通用寄存器传递。
指令示例:
1
| |
2、BKPT指令
BKPT指令的格式为:
BKPT 16位的立即数
BKPT指令产生软件断点中断,可用于程序的调试。
ARM汇编器所支持的伪指令
在ARM汇编语言程序里,有一些特殊指令助记符,这些助记符与指令系统的助记符不同,没有相对应的操作码,通常称这些特殊指令助记符为伪指令,他们所完成的操作称为伪操作。伪指令在源程序中的作用是为完成汇编程序作各种准备工作的,这些伪指令仅在汇编过程中起作用,一旦汇编结束,伪指令的使命就完成。
在ARM的汇编程序中,有如下4种伪指令:符号定义伪指令、数据定义伪指令、汇编控制伪指令、宏指令以及其他伪指令。
一、 符号定义(Symbol Definition)伪指令
符号定义伪指令用于定义ARM汇编程序中的变量、对变量赋值以及定义寄存器的别名等操作。常见的符号定义伪指令有如下4种:
1、 GBLA、GBLL和GBLS
语法格式:
GBLA(GBLL或GBLS) 全局变量名
GBLA、GBLL和GBLS伪指令用于定义一个ARM程序中的全局变量,并将其初始化。其中:
GBLA伪指令用于定义一个全局的数字变量,并初始化为0;
GBLL伪指令用于定义一个全局的逻辑变量,并初始化为F(假);
GBLS伪指令用于定义一个全局的字符串变量,并初始化为空;
由于以上三条伪指令用于定义全局变量,因此在整个程序范围内变量名必须唯一。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
2、 LCLA、LCLL和LCLS
语法格式:
LCLA(LCLL或LCLS) 局部变量名
LCLA、LCLL和LCLS伪指令用于定义一个ARM程序中的局部变量,并将其初始化。其中:
LCLA伪指令用于定义一个局部的数字变量,并初始化为0;
LCLL伪指令用于定义一个局部的逻辑变量,并初始化为F(假);
LCLS伪指令用于定义一个局部的字符串变量,并初始化为空;
以上三条伪指令用于声明局部变量,在其作用范围内变量名必须唯一。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
3、 SETA、SETL和SETS
语法格式:
变量名 SETA(SETL或SETS) 表达式
伪指令SETA、SETL、SETS用于给一个已经定义的全局变量或局部变量赋值。
SETA伪指令用于给一个数学变量赋值;
SETL伪指令用于给一个逻辑变量赋值;
SETS伪指令用于给一个字符串变量赋值;
其中,变量名为已经定义过的全局变量或局部变量,表达式为将要赋给变量的值。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 | |
4、 RLIST
语法格式:
名称 RLIST {寄存器列表}
RLIST伪指令可用于对一个通用寄存器列表定义名称,使用该伪指令定义的名称可在ARM指令LDM/STM中使用。在LDM/STM指令中,列表中的寄存器访问次序为根据寄存器的编号由低到高,而与列表中的寄存器排列次序无关。
使用示例:
1
| |
二、数据定义(Data Definition)伪指令
数据定义伪指令一般用于为特定的数据分配存储单元,同时可完成已分配存储单元的初始化。常见的数据定义伪指令有如下9种:
1、 DCB
语法格式:
标号 DCB 表达式
DCB伪指令用于分配一片连续的字节存储单元并用伪指令中指定的表达式初始化。其中,表达式可以为0~255的数字或字符串。DCB也可用“=”代替。
使用示例:
1
| |
2、 DCW(或DCWU)
语法格式:
标号 DCW(或DCWU) 表达式
DCW(或DCWU)伪指令用于分配一片连续的半字存储单元并用伪指令中指定的表达式初始化。其中,表达式可以为程序标号或数字表达式。
用DCW分配的字存储单元是半字对齐的,而用DCWU分配的字存储单元并不严格半字对齐。
使用示例:
1
| |
3、 DCD(或DCDU)
语法格式:
标号 DCD(或DCDU) 表达式
DCD(或DCDU)伪指令用于分配一片连续的字存储单元并用伪指令中指定的表达式初始化。其中,表达式可以为程序标号或数字表达式。DCD也可用“&”代替。
用DCD分配的字存储单元是字对齐的,而用DCDU分配的字存储单元并不严格字对齐。
使用示例:
1
| |
4、 DCFD(或DCFDU)
语法格式:
标号 DCFD(或DCFDU) 表达式
DCFD(或DCFDU)伪指令用于为双精度的浮点数分配一片连续的字存储单元并用伪指令中指定的表达式初始化。每个双精度的浮点数占据两个字单元。
用DCFD分配的字存储单元是字对齐的,而用DCFDU分配的字存储单元并不严格字对齐。
使用示例:
1
| |
5、 DCFS(或DCFSU)
语法格式:
标号 DCFS(或DCFSU) 表达式
DCFS(或DCFSU)伪指令用于为单精度的浮点数分配一片连续的字存储单元并用伪指令中指定的表达式初始化。每个单精度的浮点数占据一个字单元。
用DCFS分配的字存储单元是字对齐的,而用DCFSU分配的字存储单元并不严格字对齐。
使用示例:
1
| |
6、 DCQ(或DCQU)
语法格式:
标号 DCQ(或DCQU) 表达式
DCQ(或DCQU)伪指令用于分配一片以8个字节为单位的连续存储区域并用伪指令中指定的表达式初始化。
用DCQ分配的存储单元是字对齐的,而用DCQU分配的存储单元并不严格字对齐。
使用示例:
1
| |
7、 SPACE
语法格式:
标号 SPACE 表达式
SPACE伪指令用于分配一片连续的存储区域并初始化为0。其中,表达式为要分配的字节数。SPACE也可用“%”代替。
使用示例:
1
| |
8、 MAP
语法格式:
MAP 表达式{,基址寄存器}
MAP伪指令用于定义一个结构化的内存表的首地址。MAP也可用“^”代替。
表达式可以为程序中的标号或数学表达式,基址寄存器为可选项,当基址寄存器选项不存在时,表达式的值即为内存表的首地址,当该选项存在时,内存表的首地址为表达式的值与基址寄存器的和。
MAP伪指令通常与FIELD伪指令配合使用来定义结构化的内存表。
使用示例:
1
| |
9、 FILED
语法格式:
标号 FIELD 表达式
FIELD伪指令用于定义一个结构化内存表中的数据域。FILED也可用“#”代替。
表达式的值为当前数据域在内存表中所占的字节数。
FIELD伪指令常与MAP伪指令配合使用来定义结构化的内存表。MAP伪指令定义内存表的首地址,FIELD伪指令定义内存表中的各个数据域,并可以为每个数据域指定一个标号供其他的指令引用。
注意MAP和FIELD伪指令仅用于定义数据结构,并不实际分配存储单元。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 | |
三、 汇编控制(Assembly Control)伪指令
汇编控制伪指令用于控制汇编程序的执行流程,常用的汇编控制伪指令包括以下4条:
1、 IF、ELSE、ENDIF
语法格式:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
IF、ELSE、ENDIF伪指令能根据条件的成立与否决定是否执行某个指令序列。当IF后面的逻辑表达式为真,则执行指令序列1,否则执行指令序列2。其中,ELSE及指令序列2可以没有,此时,当IF后面的逻辑表达式为真,则执行指令序列1,否则继续执行后面的指令。
IF、ELSE、ENDIF伪指令可以嵌套使用。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | |
2、 WHILE、WEND
语法格式:
1 2 3 | |
WHILE、WEND伪指令能根据条件的成立与否决定是否循环执行某个指令序列。当WHILE后面的逻辑表达式为真,则执行指令序列,该指令序列执行完毕后,再判断逻辑表达式的值,若为真则继续执行,一直到逻辑表达式的值为假。
WHILE、WEND伪指令可以嵌套使用。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
3、 MACRO、MEND
语法格式:
$标号 宏名 $参数1,$参数2,……
指令序列
MEND
MACRO、MEND伪指令可以将一段代码定义为一个整体,称为宏指令,然后就可以在程序中通过宏指令多次调用该段代码。其中,$标号在宏指令被展开时,标号会被替换为用户定义的符号,宏指令可以使用一个或多个参数,当宏指令被展开时,这些参数被相应的值替换。
宏指令的使用方式和功能与子程序有些相似,子程序可以提供模块化的程序设计、节省存储空间并提高运行速度。但在使用子程序结构时需要保护现场,从而增加了系统的开销,因此,在代码较短且需要传递的参数较多时,可以使用宏指令代替子程序。
包含在MACRO和MEND之间的指令序列称为宏定义体,在宏定义体的第一行应声明宏的原型(包含宏名、所需的参数),然后就可以在汇编程序中通过宏名来调用该指令序列。在源程序被编译时,汇编器将宏调用展开,用宏定义中的指令序列代替程序中的宏调用,并将实际参数的值传递给宏定义中的形式参数。
MACRO、MEND伪指令可以嵌套使用。
4、 MEXIT
语法格式:
MEXIT
MEXIT用于从宏定义中跳转出去。
四、其他常用的伪指令
还有一些其他的伪指令,在汇编程序中经常会被使用,包括以下13条:
1、 AREA
语法格式:
AREA 段名 属性1,属性2,……
AREA伪指令用于定义一个代码段或数据段。其中,段名若以数字开头,则该段名需用“|”括起来,如|1_test|。
属性字段表示该代码段(或数据段)的相关属性,多个属性用逗号分隔。常用的属性如下:
●CODE属性:用于定义代码段,默认为READONLY。
●DATA属性:用于定义数据段,默认为READWRITE。
●READONLY属性:指定本段为只读,代码段默认为READONLY。
●READWRITE属性:指定本段为可读可写,数据段的默认属性为READWRITE。
●ALIGN属性:使用方式为ALIGN 表达式。在默认时,ELF(可执行连接文件)的代码段和数据段是按字对齐的,表达式的取值范围为0~31,相应的对齐方式为2表达式次方。
●COMMON属性:该属性定义一个通用的段,不包含任何的用户代码和数据。各源文件中同名的COMMON段共享同一段存储单元。
一个汇编语言程序至少要包含一个段,当程序太长时,也可以将程序分为多个代码段和数据段。
使用示例:
1 2 | |
2、 ALIGN
语法格式:
ALIGN {表达式{,偏移量}}
ALIGN伪指令可通过添加填充字节的方式,使当前位置满足一定的对其方式|。其中,表达式的值用于指定对齐方式,可能的取值为2的幂,如1、2、4、 8、16等。若未指定表达式,则将当前位置对齐到下一个字的位置。偏移量也为一个数字表达式,若使用该字段,则当前位置的对齐方式为:2的表达式次幂+偏移量。
使用示例:
1 2 3 | |
3、 CODE16、CODE32
语法格式:
CODE16(或CODE32)
CODE16伪指令通知编译器,其后的指令序列为16位的Thumb指令。
CODE32伪指令通知编译器,其后的指令序列为32位的ARM指令。
若在汇编源程序中同时包含ARM指令和Thumb指令时,可用CODE16伪指令通知编译器其后的指令序列为16位的Thumb指令,CODE32伪指令通知编译器其后的指令序列为32位的ARM指令。因此,在使用ARM指令和Thumb指令混合编程的代码里,可用这两条伪指令进行切换,但注意他们只通知编译器其后指令的类型,并不能对处理器进行状态的切换。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | |
4、 ENTRY
语法格式:
ENTRY
ENTRY伪指令用于指定汇编程序的入口点。在一个完整的汇编程序中至少要有一个ENTRY(也可以有多个,当有多个ENTRY时,程序的真正入口点由链接器指定),但在一个源文件里最多只能有一个ENTRY(可以没有)。
使用示例:
1 2 3 | |
5、 END
语法格式:
END
END伪指令用于通知编译器已经到了源程序的结尾。
使用示例:
1 2 3 | |
6、 EQU
语法格式:
名称 EQU 表达式{,类型}
EQU伪指令用于为程序中的常量、标号等定义一个等效的字符名称,类似于C语言中的#define。其中EQU可用“*”代替。
名称为EQU伪指令定义的字符名称,当表达式为32位的常量时,可以指定表达式的数据类型,可以有以下三种类型:
CODE16、CODE32和DATA
使用示例:
1 2 | |
7、 EXPORT(或GLOBAL)
语法格式:
EXPORT 标号{[WEAK]}
EXPORT伪指令用于在程序中声明一个全局的标号,该标号可在其他的文件中引用。EXPORT可用GLOBAL代替。标号在程序中区分大小写,[WEAK]选项声明其他的同名标号优先于该标号被引用。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 | |
8、 IMPORT
语法格式:
IMPORT 标号{[WEAK]}
IMPORT伪指令用于通知编译器要使用的标号在其他的源文件中定义,但要在当前源文件中引用,而且无论当前源文件是否引用该标号,该标号均会被加入到当前源文件的符号表中。
标号在程序中区分大小写,[WEAK]选项表示当所有的源文件都没有定义这样一个标号时,编译器也不给出错误信息,在多数情况下将该标号置为0,若该标号为B或BL指令引用,则将B或BL指令置为NOP操作。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
9、 EXTERN
语法格式:
EXTERN 标号{[WEAK]}
EXTERN伪指令用于通知编译器要使用的标号在其他的源文件中定义,但要在当前源文件中引用,如果当前源文件实际并未引用该标号,该标号就不会被加入到当前源文件的符号表中。
标号在程序中区分大小写,[WEAK]选项表示当所有的源文件都没有定义这样一个标号时,编译器也不给出错误信息,在多数情况下将该标号置为0,若该标号为B或BL指令引用,则将B或BL指令置为NOP操作。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
10、GET(或INCLUDE)
语法格式:
GET 文件名
GET伪指令用于将一个源文件包含到当前的源文件中,并将被包含的源文件在当前位置进行汇编处理。可以使用INCLUDE代替GET。
汇编程序中常用的方法是在某源文件中定义一些宏指令,用EQU定义常量的符号名称,用MAP和FIELD定义结构化的数据类型,然后用GET伪指令将这个源文件包含到其他的源文件中。使用方法与C语言中的“include”相似。
GET伪指令只能用于包含源文件,包含目标文件需要使用INCBIN伪指令
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
11、INCBIN
语法格式:
INCBIN 文件名
INCBIN伪指令用于将一个目标文件或数据文件包含到当前的源文件中,被包含的文件不作任何变动的存放在当前文件中,编译器从其后开始继续处理。
使用示例:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
12、RN
语法格式:
名称 RN 表达式
RN伪指令用于给一个寄存器定义一个别名。采用这种方式可以方便程序员记忆该寄存器的功能。其中,名称为给寄存器定义的别名,表达式为寄存器的编码。
使用示例:
1
| |
13、ROUT
语法格式:
{名称} ROUT
ROUT伪指令用于给一个局部变量定义作用范围。在程序中未使用该伪指令时,局部变量的作用范围为所在的AREA,而使用ROUT后,局部变量的作为范围为当前ROUT和下一个ROUT之间。
4 ARM GNU常用汇编语言介绍
4.1 ARM GNU常用汇编伪指令介绍
1. abort
.abort: 停止汇编
.align absexpr1,absexpr2:
以某种对齐方式,在未使用的存储区域填充值. 第一个值表示对齐方式,4, 8,16或32. 第二个表达式值表示填充的值.
2. if…else…endif
.if
.else
.endif: 支持条件预编译
3. include
.include “file”: 包含指定的头文件, 可以把一个汇编常量定义放在头文件中.
4. comm
.comm symbol, length:在bss段申请一段命名空间,该段空间的名称叫symbol, 长度为length. Ld连接器在连接会为它留出空间.
5. data
.data subsection: 说明接下来的定义归属于subsection数据段.
6. equ
.equ symbol, expression: 把某一个符号(symbol)定义成某一个值(expression).该指令并不分配空间.
7. global
.global symbol: 定义一个全局符号, 通常是为ld使用.
8. ascii
.ascii “string”: 定义一个字符串并为之分配空间.
9. byte
.byte expressions: 定义一个字节, 并为之分配空间.
10. short
.short expressions: 定义一个短整型, 并为之分配空间.
11. int
.int expressions: 定义一个整型,并为之分配空间.
12 long
.long expressions: 定义一个长整型, 并为之分配空间.
13 word
.word expressions: 定义一个字,并为之分配空间, 4bytes.
14. macro/endm
.macro: 定义一段宏代码, .macro表示代码的开始, .endm表示代码的结束.
15. req
name .req register name: 为寄存器定义一个别名.
16. code
.code [16|32]: 指定指令代码产生的长度, 16表示Thumb指令, 32表示ARM指令.
17. ltorg
.ltorg: 表示当前往下的定义在归于当前段,并为之分配空间.
4.2 ARM GNU专有符号
1. @
表示注释从当前位置到行尾的字符.
2.
注释掉一整行.
3. ;
新行分隔符.
4.3 操作码
1. NOP
nop
空操作, 相当于MOV r0, r0
2. LDR
ldr
相当于PC寄存器或其它寄存器的长转移.
3.ADR
adr
5 可执行生成说明
5.1 lds文件说明
5.1.1 主要符号说明
OUTPUT_FORMAT(bfdname)
指定输出可执行文件格式.OUTPUT_ARCH(bfdname)
指定输出可执行文件所运行CPU平台ENTRY(symbol)
指定可执行文件的入口段
5.1.2 段定义说明
- 段定义格式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | |