我们知道,两个 N 位数字的整数的乘法,如果使用常规的算法,时间复杂度是 O(N2)。
然而,使用快速傅里叶变换,时间复杂度可以降低到 O(N logN loglogN)。
假设我们要计算以下两个 N 位数字的乘积:
1
2
a = (aN-1aN-2...a1a0)10 = aN-1x10N-1 + aN-2x10N-2 + ... + a1x101 + a0x100
b = (bN-1bN-2...b1b0)10 = bN-1x10N-1 + bN-2x10N-2 + ... + b1x101 + b0x100
将上面两个式子相乘,得到以下公式 (共 2N - 1 项):
1
c = a x b = c2N-2x102N-2 + c2N-3x102N-3 + ... + c1x101 + c0x100
非常容易验证,上式中的 ck ( 0 ≤ k ≤ 2N-2 ) 满足以下公式:
1
ck = a0xbk + a1xbk-1 + ... + ak-2xb2 + ak-1xb1 + akxb0 + ak+1xb-1 + ... + aN-2xb-(N-2-k) + aN-1xb-(N-1-k)
上式共有 N 项,ai 和 bj 的下标 i 和 j 满足 i + j = k。若不满足 0 ≤ i, j ≤ N-1 时,则令 ai = bj = 0。
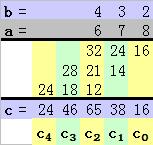
我们以两个 3 ( N = 3 ) 位数 a = 678 和 b = 432 的乘积来说明以上过程吧。
1
2
a = (678)10 = 6x102 + 7x101 + 8x100
b = (432)10 = 4x102 + 3x101 + 2x100
由此:
1
2
3
4
5
c0 = a0xb0 + a1xb-1 + a2xb-2 = 8x2 + 7x0 + 6x0 = 16 + 0 + 0 = 16
c1 = a0xb1 + a1xb0 + a2xb-1 = 8x3 + 7x2 + 6x0 = 24 + 14 + 0 = 38
c2 = a0xb2 + a1xb1 + a2xb0 = 8x4 + 7x3 +6x2 = 32 + 21 + 12 = 65
c3 = a0xb3 + a1xb2 + a2xb1 = 8x0 + 7x4 + 6x3 = 0 + 28 + 18 = 46
c4 = a0xb4 + a1xb3 + a2xb2 = 8x0 + 7x0 + 6x4 = 0 + 0 + 24 = 24
最后:
1
2
3
c = a x b = 104xc4 + 103xc3 + 102xc2 + 101xc1 + 100xc0
= 10000x24 + 1000x46 + 100x65 + 10x38 + 1x16
= 292896
如果按以上方法计算大整数的乘法,时间复杂度是 O(N2)。
但是,我们注意到,向量 {ck} 是向量 {ai} 和向量 {bj} 的卷积。
根据卷积定理,向量卷积的离散傅里叶变换是向量离散傅里叶变换的乘积。于是,我们可以按照以下步骤来计算大整数乘法:
对于复数向量 { xN-1, …, x1, x0 },离散傅里叶变换公式为:
离散傅里叶逆变换公式为:
注意到离散傅里叶逆变换除了指数的符号相反以及结果需要乘以归一化因子 1/N 外,与离散傅里叶变换是相同的。所以计算离散傅里叶变换的程序稍做修改也可以用于计算逆变换。
在我们的例子中,乘积 c = 292896,共 6 位数字,N 需要扩展到 23 = 8。那么,向量 {ai} 和向量 {bj} 如下所示:
1
2
{ a7, a6, a5, a4, a3, a2, a1, a0 } = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 6, 7, 8 }
{ b7, b6, b5, b4, b3, b2, b1, b0 } = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 3, 2 }
为了求出以上向量的离散傅里叶变换,我们令
1
ω = e-2πi/N = e-2πi/8 = e-πi/4 = cos(-π/4) + i sin(-π/4) = √2 / 2 - i √2 / 2 ≈ 0.7-0.7i
为了方便计算,我们预先求出 ω 的各次方,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ω8 = ω0 = e0 = 1
ω9 = ω1 = e-πi/4 = cos(-π/4) + i sin(-π/4) ≈ 0.7-0.7i
ω10 = ω2 = e-πi/2 = cos(-π/2) + i sin(-π/2) = -i
ω11 = ω3 = e-3πi/4 = cos(-3π/4) + i sin(-3π/4) ≈ -0.7-0.7i
ω12 = ω4 = e-πi = cos(-π) + i sin(-π) = -1
ω13 = ω5 = e-5πi/4 = cos(-5π/4) + i sin(-5π/4) ≈ -0.7+0.7i
ω14 = ω6 = e-3πi/2 = cos(-3π/2) + i sin(-3π/2) = i
ω15 = ω7 = e-7πi/4 = cos(-7π/4) + i sin(-7π/4) ≈ 0.7+0.7i
注意到当 n > 2 时,an = 0,于是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
A0 = a0xω0x0 + a1xω1x0 + a2xω2x0 = 8xω0 + 7xω0 + 6xω0 = 8x1 + 7x1 + 6x1 = 21
A1 = a0xω0x1 + a1xω1x1 + a2xω2x1 = 8xω0 + 7xω1 + 6xω2 ≈ 8x1 + 7x(0.7 - 0.7i) + 6x(-i) = 12.9-10.9i
A2 = a0xω0x2 + a1xω1x2 + a2xω2x2 = 8xω0 + 7xω2 + 6xω4 = 8x1 + 7x(-i) + 6x(-1) = 2-7i
A3 = a0xω0x3 + a1xω1x3 + a2xω2x3 = 8xω0 + 7xω3 + 6xω6 ≈ 8x1 + 7x(-0.7 - 0.7i) + 6xi = 3.1+1.1i
A4 = a0xω0x4 + a1xω1x4 + a2xω2x4 = 8xω0 + 7xω4 + 6xω8 = 8x1 + 7x(-1) + 6x1 = 7
A5 = a0xω0x5 + a1xω1x5 + a2xω2x5 = 8xω0 + 7xω5 + 6xω10 ≈ 8x1 + 7x(-0.7 + 0.7i) + 6x(-i) = 3.1-1.1i
A6 = a0xω0x6 + a1xω1x6 + a2xω2x6 = 8xω0 + 7xω6 + 6xω12 = 8x1 + 7xi + 6x(-1) = 2+7i
A7 = a0xω0x7 + a1xω1x7 + a2xω2x7 = 8xω0 + 7xω7 + 6xω14 ≈ 8x1 + 7x(0.7 + 0.7i) + 6xi = 12.9+10.9i
同样,当 n > 2 时,bn = 0,于是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
B0 = b0xω0x0 + b1xω1x0 + b2xω2x0 = 2xω0 + 3xω0 + 4xω0 = 2x1 + 3x1 + 4x1 = 9
B1 = b0xω0x1 + b1xω1x1 + b2xω2x1 = 2xω0 + 3xω1 + 4xω2 ≈ 2x1 + 3x(0.7 - 0.7i) + 4x(-i) = 4.1-6.1i
B2 = b0xω0x2 + b1xω1x2 + b2xω2x2 = 2xω0 + 3xω2 + 4xω4 = 2x1 + 3x(-i) + 4x(-1) = -2-3i
B3 = b0xω0x3 + b1xω1x3 + b2xω2x3 = 2xω0 + 3xω3 + 4xω6 ≈ 2x1 + 3x(-0.7 - 0.7i) + 4xi = -0.1+1.9i
B4 = b0xω0x4 + b1xω1x4 + b2xω2x4 = 2xω0 + 3xω4 + 4xω8 = 2x1 + 3x(-1) + 4x1 = 3
B5 = b0xω0x5 + b1xω1x5 + b2xω2x5 = 2xω0 + 3xω5 + 4xω10 ≈ 2x1 + 3x(-0.7 + 0.7i) + 4x(-i) = -0.1-1.9i
B6 = b0xω0x6 + b1xω1x6 + b2xω2x6 = 2xω0 + 3xω6 + 4xω12 = 2x1 + 3xi + 4x(-1) = -2+3i
B7 = b0xω0x7 + b1xω1x7 + b2xω2x7 = 2xω0 + 3xω7 + 4xω14 ≈ 2x1 + 3x(0.7 + 0.7i) + 4xi = 4.1+6.1i
这样,向量 {ai} 和向量 {bj} 的离散傅里叶变换 {Ai} 和 {Bj} 如下所示:
1
2
{ A7, A6, A5, A4, A3, A2, A1, A0 } = { 12.9+10.9i, 2+7i, 3.1-1.1i, 7, 3.1+1.1i, 2-7i, 12.9-10.9i, 21 }
{ B7, B6, B5, B4, B3, B2, B1, B0 } = { 4.1+6.1i, -2+3i, -0.1-1.9i, 3, -0.1+1.9i, -2-3i, 4.1-6.1i, 9 }
现在,将她们逐项相乘得到向量 {Ck},即
1
{ C7, C6, C5, C4, C3, C2, C1, C0 } = { -13.6+123.4i, -25-8i, -2.4-5.8i, 21, -2.4+5.8i, -25+8i, -13.6-123.4i, 189 }
为了求出向量 {Ck} 的离散傅里叶逆变换,我们令
1
ω = e2πi/N = e2πi/8 = eπi/4 = cos(π/4) + i sin(π/4) = √2 / 2 + i √2 / 2 ≈ 0.7+0.7i
为了方便计算,我们预先求出 ω 的各次方(注意 ωk+8 = ωk),如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ω0 = e0 = 1
ω1 = eπi/4 = cos(π/4) + i sin(π/4) ≈ 0.7+0.7i
ω2 = eπi/2 = cos(π/2) + i sin(π/2) = i
ω3 = e3πi/4 = cos(3π/4) + i sin(3π/4) ≈ -0.7+0.7i
ω4 = eπi = cos(π) + i sin(π) = -1
ω5 = e5πi/4 = cos(5π/4) + i sin(5π/4) ≈ -0.7-0.7i
ω6 = e3πi/2 = cos(3π/2) + i sin(3π/2) = -i
ω7 = e7πi/4 = cos(7π/4) + i sin(7π/4) ≈ 0.7-0.7i
于是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
c0 = (1/N) x ( C0xω0x0 + C1xω1x0 + C2xω2x0 + C3xω3x0
+ C4xω4x0 + C5xω5x0 + C6xω6x0 + C7xω7x0 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + (-13.6-123.4i)xω0 + (-25+8i)xω0 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω0
+ 21xω0 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω0 + (-25-8i)xω0 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω0 )
= 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x1 + (-25+8i)x1 + (-2.4+5.8i)x1
+ 21x1 + (-2.4-5.8i)x1 + (-25-8i)x1 + (-13.6+123.4i)x1 )
= 0.125 x 128 = 16
c1 = (1/N) x ( 8xc1 = C0xω0x1 + C1xω1x1 + C2xω2x1 + C3xω3x1
+ C4xω4x1 + C5xω5x1 + C6xω6x1 + C7xω7x1 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + ( -13.6-123.4i)xω1 + (-25+8i)xω2 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω3
+ 21xω4 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω5 + (-25-8i)xω6 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω7 )
≈ 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x(0.7+0.7i) + (-25+8i)x(i) + (-2.4+5.8i)x(-0.7+0.7i)
+ 21x(-1) + (-2.4-5.8i)x(-0.7-0.7i) + (-25-8i)x(-i) + (-13.6+123.4i)x(0.7-0.7i) )
= 0.125 x 300.96 = 37.62 ≈ 38
c2 = (1/N) x ( C0xω0x2 + C1xω1x2 + C2xω2x2 + C3xω3x2
+ C4xω4x2 + C5xω5x2 + C6xω6x2 + C7xω7x2 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + (-13.6-123.4i)xω2 + (-25+8i)xω4 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω6
+ 21xω8 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω10 + (-25-8i)xω12 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω14 )
= 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x(i) + (-25+8i)x(-1) + (-2.4+5.8i)x(-i)
+ 21x1 + (-2.4-5.8i)x(i) + (-25-8i)x(-1) + (-13.6+123.4i)x(-i) )
≈ 0.125 x 518.4 = 64.8 ≈ 65
c3 = (1/N) x ( C0xω0x3 + C1xω1x3 + C2xω2x3 + C3xω3x3
+ C4xω4x3 + C5xω5x3 + C6xω6x3 + C7xω7x3 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + (-13.6-123.4i)xω3 + (-25+8i)xω6 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω9
+ 21xω12 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω15 + (-25-8i)xω18 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω21 )
≈ 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x(-0.7+0.7i) + (-25+8i)x(-i) + (-2.4+5.8i)x(0.7+0.7i)
+ 21x(-1) + (-2.4-5.8i)x(0.7-0.7i) + (-25-8i)x(i) + (-13.6+123.4i)x(-0.7-0.7i) )
= 0.125 x 364.32 = 45.54 ≈ 46
c4 = (1/N) x ( C0xω0x4 + C1xω1x4 + C2xω2x4 + C3xω3x4
+ C4xω4x4 + C5xω5x4 + C6xω6x4 + C7xω7x4 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + (-13.6-123.4i)xω4 + (-25+8i)xω8 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω12
+ 21xω16 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω20 + (-25-8i)xω24 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω28 )
= 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x(-1) + (-25+8i)x1 + (-2.4+5.8i)x(-1)
+ 21x1 + (-2.4-5.8i)x(-1) + (-25-8i)x1 + (-13.6+123.4i)x(-1) )
= 0.125 x 192 = 24
c5 = (1/N) x ( C0xω0x5 + C1xω1x5 + C2xω2x5 + C3xω3x5
+ C4xω4x5 + C5xω5x5 + C6xω6x5 + C7xω7x5 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + (-13.6-123.4i)xω5 + (-25+8i)xω10 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω15
+ 21xω20 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω25 + (-25-8i)xω30 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω35 )
≈ 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x(-0.7-0.7i) + (-25+8i)x(i) + (-2.4+5.8i)x(0.7-0.7i)
+ 21x(-1) + (-2.4-5.8i)x(0.7+0.7i) + (-25-8i)x(-i) + (-13.6+123.4i)x(-0.7+0.7i) )
= 0.125 x 3.04 = 0.38 ≈ 0
c6 = (1/N) x ( C0xω0x6 + C1xω1x6 + C2xω2x6 + C3xω3x6
+ C4xω4x6 + C5xω5x6 + C6xω6x6 + C7xω7x6 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + (-13.6-123.4i)xω6 + (-25+8i)xω12 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω18
+ 21xω24 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω30 + (-25-8i)xω36 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω42 )
= 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x(-i) + (-25+8i)x(-1) + (-2.4+5.8i)x(i)
+ 21x1 + (-2.4-5.8i)x(-i) + (-25-8i)x(-1) + (-13.6+123.4i)x(i) )
= 0.125 x 1.6 = 0.2 ≈ 0
c7 = (1/N) x ( C0xω0x7 + C1xω1x7 + C2xω2x7 + C3xω3x7
+ C4xω4x7 + C5xω5x7 + C6xω6x7 + C7xω7x7 )
= (1/8) x ( 189xω0 + (-13.6-123.4i)xω7 + (-25+8i)xω14 + (-2.4+5.8i)xω21
+ 21xω28 + (-2.4-5.8i)xω35 + (-25-8i)xω42 + (-13.6+123.4i)xω49 )
≈ 0.125 x ( 189x1 + (-13.6-123.4i)x(0.7-0.7i) + (-25+8i)x(-i) + (-2.4+5.8i)x(-0.7-0.7i)
+ 21x(-1) + (-2.4-5.8i)x(-0.7+0.7i) + (-25-8i)x(i) + (-13.6+123.4i)x(0.7+0.7i) )
= 0.125 x 3.68 = 0.46 ≈ 0
这样,我们就使用离散傅里叶变换和逆变换计算出了向量 {ai} 和向量 {bj} 的卷积向量 {ck},如下所示:
1
{ c7, c6, c5, c4, c3, c2, c1, c0 } = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 24, 46, 65, 38, 16 }
这和我们在前面直接使用向量 {ai} 和向量 {bj} 来计算卷积的结果是一样的。
但是,这个算法的时间复杂度还是 O(N2)。我们绕了这么一大圈,不是白费劲了吗?
现在就到了关键时刻
关键在于:直接进行离散傅里叶变换的计算复杂度是 O(N2)。快速傅里叶变换可以计算出与直接计算相同的结果,但只需要 O(N logN) 的计算复杂度。 N logN 和 N2 之间的差别是巨大的。例如,当 N = 106 时,在一个每秒运算百万次的计算机上,粗略地说,它们之间就是占用 30 秒 CPU 时间和两星期 CPU 时间的差别。
快速傅里叶变换的要点如下:
一个界长为 N 的离散傅里叶变换可以重新写成两个界长各为 N/2 的离散傅里叶变换之和。其中一个变换由原来 N 个点中的偶数点构成,另一个变换由奇数点构成。这个过程可以递归地进行下去,直到我们将全部数据细分为界长为 1 的变换。什么是界长为 1 的傅里叶变换呢?它正是把一个输入值复制成它的一个输出值的恒等运算。要实现以上算法,最容易的情况是原始的 N 为 2 的整幂次项,如果数据集的界长不是 2 的幂次时,则可添上一些零值,直到 2 的下一幂次。在这个算法中,每递归一次需 N 阶运算,共需要 log N 次递归,所以快速傅里叶变换算法的时间复杂度是 O(N logN)。
由于快速傅里叶变换是采用了浮点运算,因此我们需要足够的精度,以使在出现舍入误差时,结果中每个组成部分的准确整数值仍是可辨认的。长度为 N 的 B 进制数可产生大到 B2N 阶的卷积分量。我们知道,双精度浮点数的尾数是 53 个二进位,所以:
2 x log2B + log2N + 几个 x log2log2N < 53
上式中左边最后一项是为了快速傅里叶变换的舍入误差。
所以,为了能够计算尽量大的整数,一般 B 不会取得太大。在计算机程序中经常使用 256 进制进行运算。但是如果经常需要将计算结果和十进制互相转换,则往往使用 100 进制进行运算。
快速傅里叶变换:
FFT算法设计的基本思想,就是充分利用DFT的周期性和对称性,减少重复的计算量;并把N点长序列分成几个短序列,减少每个序列长度,可大大减少计算量。
本文重点介绍其中的时域抽取法快速傅里叶变换(DIT-FFT),算法设计思想要点如下:
注意:上式仅是X(k)的前一半即N/2点运算,整个N点DFT结果还要加上后一半计算。如果老老实实计算后一半N/2点DFT,则并没有减少任何计算量。但考虑可利用DFT及其变换因子的周期性和对称性,并利用前一半计算结果,后一半计算可表示为
注意:


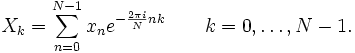
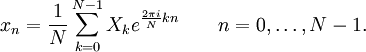
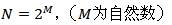 (5)
(5)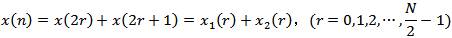 (6)
(6)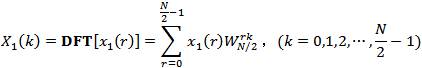 (7)
(7)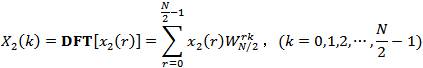 (8)
(8)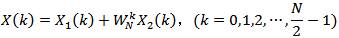 (9)
(9)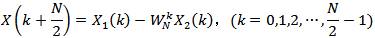 (10)
(10)