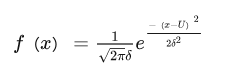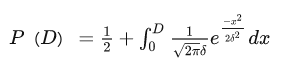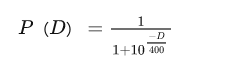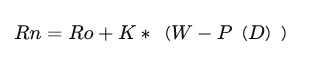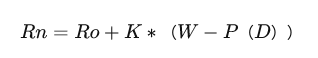https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/57480433
ELO算法原理
预期胜率计算公式
ELO算法基于这样一种假设:一名选手的当前实力受各种因素的影响会在一定范围内波动,某个时刻的用来描述其实力的函数应当符合正态分布:
其中U代表选手的实力平均水平,δ代表实力的稳定性。
经过计算,可以得出两名选手进行对战时的预期胜率:
D为两者的分差。
利用了最小二乘法,我们可以得到与它的函数图向相近的另外的一个函数,这也是我们实际运时更常用的函数:
(里面的常数项都是曲线拟合的结果,是符合上述统计学规律的,别瞎改)
即当玩家A与玩家B的分差为D时,玩家A对玩家B的期望胜率为P(D)。
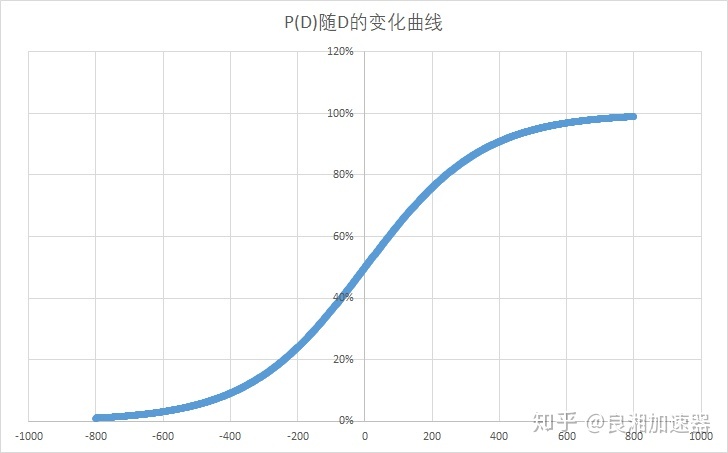
玩家分数相同时,对战预期胜率为50%,分差越大,玩家之间的胜率差距也就越大,当分差大于400时,低分玩家的预期胜率将不足10%。
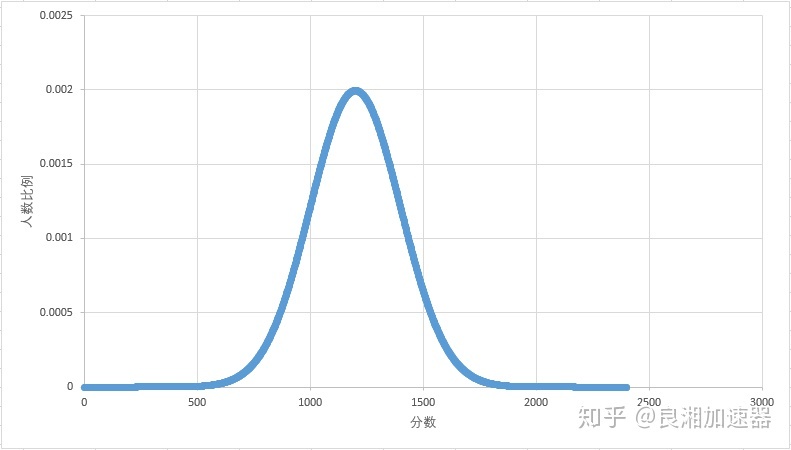
显然的,我们的玩家的游戏水平的分布也应当是一个正态分布,即大部分玩家的游戏水平都处于平均值附近,游戏水平顶尖或非常菜的人会是少数。
假如我们认为1200分是玩家的平均水平,则所有玩家的各分值分布情况将大致如下图:
各分段玩家比例分布示意图
分数迭代公式
那我们会面临下一个问题:如何知道某个玩家到底是多少分的?
毕竟我们不能用某种机器直接插入玩家大脑测试他的游戏水平吧?
对此,我们的办法是,通过玩家与不同分数的玩家的大量比赛结果,对玩家的分数进行不断地加减修正,直到玩家的分数收敛到其相应的真实水平分数。
下面我们计算玩家在一场比赛后的加减分情况。
玩家在进行一场比赛后的新分数为:
Rn是玩家比赛结束后的新的排位分值。
Ro是比赛前玩家的排位分。
K是一个加成系数,由玩家当前分值水平决定(分值越高K越小)。
W是玩家实际对局结果得分(赢=1,输=0)。
P(D)是预期胜率。
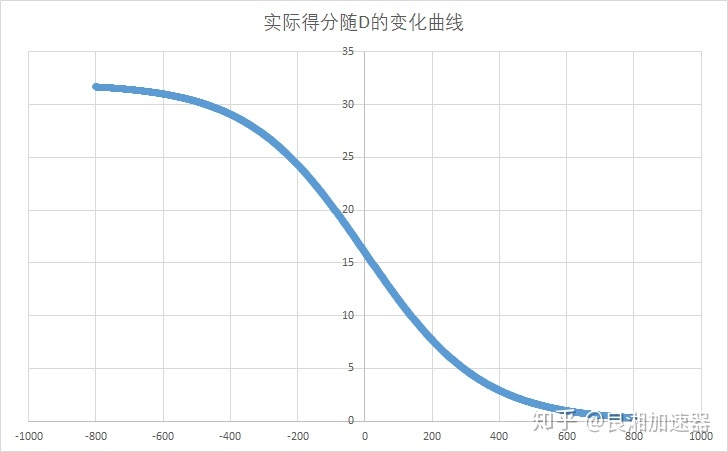
取K=32时,玩家结束一场比赛后的实际得分数如图所示。可以看到玩家战胜比自己低800分的选手后(有近100%的胜率)基本不得分。(这让我想起了守望韩服的猪皇evermore,4950分后打完了一局只加了1分)
ELO算法应用
匹配策略
以1V1的匹配为例,一般来说遵循以下匹配原则
0~N1秒内,仅匹配分差在X1以内的队友
若N1秒内未找到满足条件对手,放宽匹配条件,N1~N2秒内,仅匹配分差在X2(X2>X1)以内的对手
……
直到找到对手。
收敛期快速收敛
从上面的描述我们可以知道,玩家的一次又一次的比赛过程就是其游戏分数向其真实水平分数收敛的过程。
那么当玩家的游戏分数与真实水平分数相差过大时,其收敛期耗时也会增加,而这一时期参与游戏的玩家的游戏体验都会受到不同程度的影响。
所以我们需要一些特殊的机制来减少这段收敛期。接下来我们按照不同的情况进行讨论。
1、定位赛阶段
当一个新玩家加入游戏时,我们肯定无法得知其真实的游戏水平,只能默认他为1200分(平均值)。
为了缩短其收敛期,我们会加入定位赛的设计。
在定位赛局数内,计算玩家得分的K值将再被乘上一个系数。
2、玩家(账号)实力大幅波动
首先,我们会引入一个【连胜/连败分数加值】的变量。
当玩家连续获胜或者连续失败N次时,我们有理由相信玩家的游戏分数与真实水平分数相差过大,并按照连胜/连败局数去增加【连胜/连败分数加值】
于是在进行匹配索敌时,将按照【玩家游戏分数】+【连胜/连败分数加值】进行索敌。
(这就是守望一个3000玩家10连胜后到了3300分,但是开始匹配到3500+分玩家的原因)
最后进行分数结算时,按照【玩家游戏分数】进行。
3、休眠期的分数衰减
分数衰减的原因是:
(1)我们期望玩家的活跃参与。
(2)我们认为高分段玩家在长时间未进行游戏后,其真实水平也会下降。
所以,一般我们会设计1800分以上的玩家,X天未进行排位后其游戏分数会以Y分/天的速度衰减。
多对多的拓展
ELO积分初期是针对象棋选手而定的,所以考虑的都是象棋选手1V1的情况。但是在NVN的游戏排位赛中,需要进行一些特殊的处理。
在多人比赛中,最终得分为:
其中,Rn、Ro、K、W的值都不用处理。
对P(D)处理如下:
低分段打破零和
在之前的讨论中,我们可以很明显的发现:
对于同分段玩家来说,因为K值都是一样的,所以赢方加的分恰好等于输方扣的分。
(玩家能上分是因为把人家的分吃了,大鱼吃小鱼小鱼吃虾米,于是最后所有玩家的分数就成了正态分布)
即所有的分数是零和的。
现在的游戏中,一般会期望玩家玩得多了还是能出坑的,即就算你水平略低于平均线,你也可以玩很多局跳出低分段。
于是我们将在低分段(比如1000以下)将胜负方的K值分离。
即胜方的加分按照K1进行。
负方的扣分按照K2进行。
当K1>K2时,零和将被打破,玩家的分数分布中1000分以下的玩家数量将显著减少。
ELO积分的包装与隐藏
ELO积分对玩家水平的精确指示会打击玩家的信心,分值收敛结束后,再进行更多的对局几乎不会有任何提高(除非找了代练或者自己不知道为啥突然打通任督二脉)。
所以我们将玩家真实水平隐藏,并用一些模糊柔和的方式去告诉玩家他当前的水平(按照ELO分数包装为青铜白银黄金白金钻石)。
但记得,ELO分不会消失,从显示变成了隐藏,我们的一切计算还是以ELO分数为依据。